Measurements of inclusive D0-meson production in Ru+Ru and Zr+Zr collisions at 200 GeV
Measurements of inclusive D0-meson production in Ru+Ru and Zr+Zr collisions at √sNN = 200 GeV
PAs: Yuan Su, Yifei Zhang, Xiaolong Chen
Target Journal: European Physical Journal C (EPJ C)
Abstract:
We report the first measurements of D0-meson production at mid-rapidity (|y| < 1) in isobar collisions (96Ru+96Ru and 96Zr+96Zr) at √sNN = 200 GeV with the STAR experiment. D0 pT differential invariant yield with transverse momentum pT < 8 GeV/c are reported in 0-10%, 10-40% and 40-80% centrality. The D0 production cross section follows the number of binary collisions scaling within systematic uncertainties between isobar and Au+Au collisions at 200 GeV. The strong suppression D0 nuclear modification factor RAA is also observed for pT > 3 GeV/c in the central isobar collisions, demonstrating that charm quarks suffer significant energy loss in the bulk QCD medium. And model calculations reproduce the feature of RAA measured at 200 GeV.
GPC:
- Chairperson: Daniel Kikola
- Member(s) at large: Guannan Xie
- Member for English/Grammar QA: Helen Caines
- Member for Code QA: Diptanil Roy
- PWG representative: Isaac Mooney
- PA representative(s): Yuan Su
1st GPC meetings:
- Wednesday, Jul 31, 2024 09:00 EST
- Zoom Meeting ID: 617 6534 2307
- GPC v1 comments: https://drupal.star.bnl.gov/STAR/system/files/1st_GPC_response_D0_RAA_isobar.pdf
2nd GPC meetings:
- Wednesday, Oct 16, 2024 09:00 EST
- Zoom Meeting ID: 637 6850 5612
- GPC v2 comments: https://drupal.star.bnl.gov/STAR/system/files/GPC_4_RAA_Npart_check_0.pdf
3rd GPC meetings replies:
- Wednesday, Mar 26, 2025 01:00 EST
- GPC paper draft replies: https://drupal.star.bnl.gov/STAR/system/files/GPC_comments_replies_03262025.pdf
- Thursday, Apr 24, 2025 03:30 EST
- GPC paper draft replies: https://drupal.star.bnl.gov/STAR/system/files/GPC_replies_04242025.pdf
- Tuesday, May 27, 2025 11:30 EST
- GPC paper draft replies: https://drupal.star.bnl.gov/STAR/system/files/GPC_replies_05282025.pdf
Paper draft:
- https://drupal.star.bnl.gov/STAR/system/files/European_Physical_Journal_C__EPJ_C__20250424.pdf (---New---)
- https://drupal.star.bnl.gov/STAR/system/files/European_Physical_Journal_C__EPJ_C__20250326.pdf
- https://drupal.star.bnl.gov/STAR/system/files/European%20Physical%20Journal%20C%20%28EPJ%20C%29%2020241205.pdf
- https://drupal.star.bnl.gov/STAR/system/files/diff_24.pdf
- https://drupal.star.bnl.gov/STAR/system/files/European_Physical_Journal_C__EPJ_C__20240825.pdf
- https://drupal.star.bnl.gov/STAR/system/files/European_Physical_Journal_C__EPJ_C__05162024.pdf
Comments on previous drafts:
- Yi: https://drupal.star.bnl.gov/STAR/system/files/PWC_response_Yi.pdf
- Isaac: https://drupal.star.bnl.gov/STAR/system/files/PWC_response_Isaac.pdf
- Nihar: https://drupal.star.bnl.gov/STAR/system/files/PWC_response_Nihar.pdf
Paper code directory:
- https://drupal.star.bnl.gov/STAR/system/files/Code_QA_08022025.pdf
- https://www.star.bnl.gov/cgi-bin/protected/viewvc.cgi/cvsroot/offline/paper/psn0835/
Analysis note:
- https://drupal.star.bnl.gov/STAR/system/files/D0_RAA_in_Isobar_Ana_Note_20240825.pdf (---New---)
- https://drupal.star.bnl.gov/STAR/system/files/D0_RAA_in_Isobar_Ana_Note_0.pdf
Paper proposal talk:
- https://drupal.star.bnl.gov/STAR/system/files/Paper_Proposal_04192023.pdf
Figures:
|
|
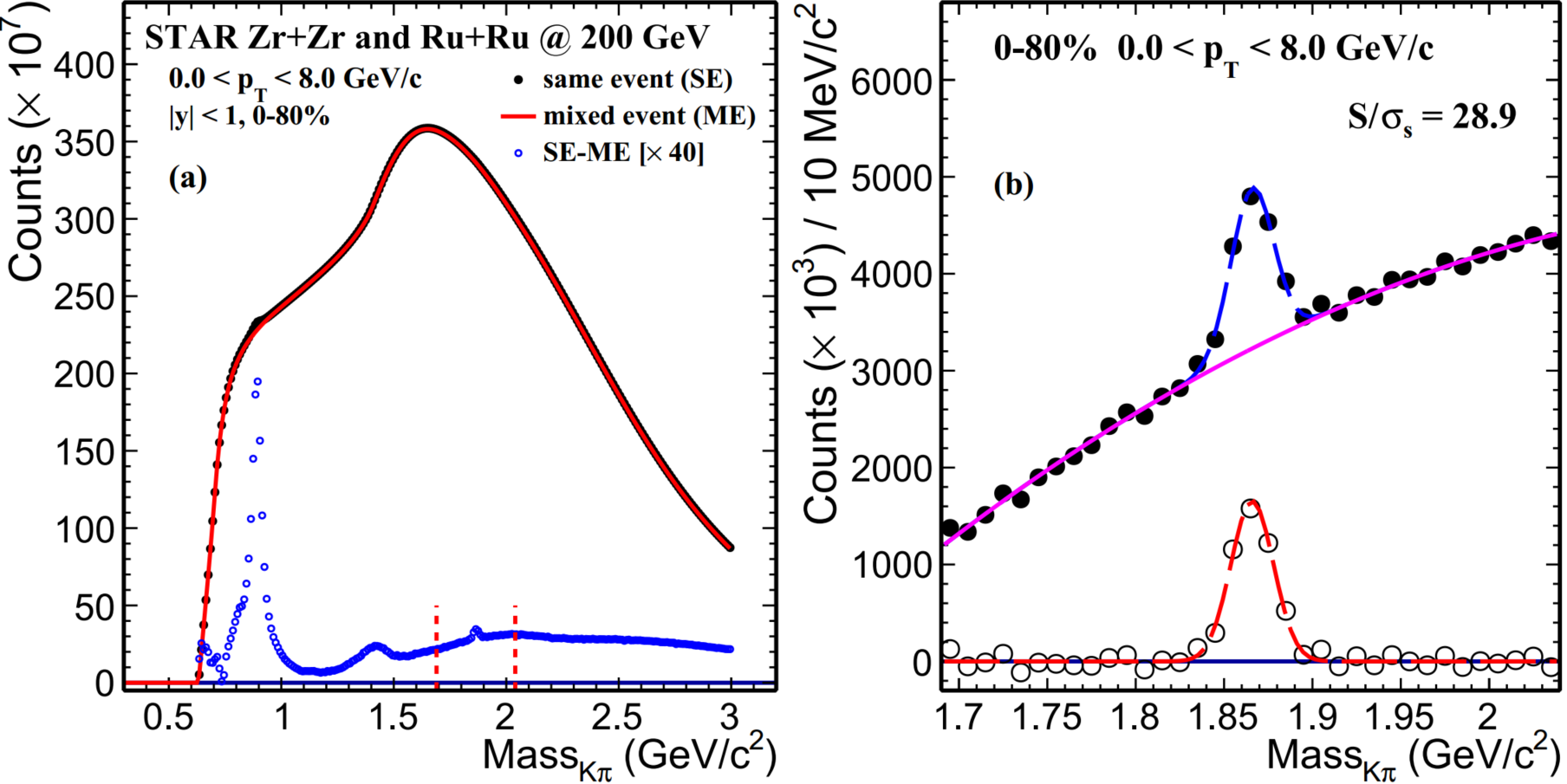
| Figure 1. The K, π invariant mass distribution with centrality 0-80% and pT range 0-8 GeV/c at mid-rapidity. In figure (a), the black solid circles depict the unlike-sign distribution under the same event, the red line shows that the mix-event method can well reproduce the combination background and the open blue circles represent the invariant mass distribution after removing the combination background. In figure (b), a Gaussian and quadratic polynomial combination function fitting (blue dash line) is applied to extract D0 raw yield. The signal significance is 28.9 for pT range 0-8 GeV/c within 0-80% centrality. |
|
|
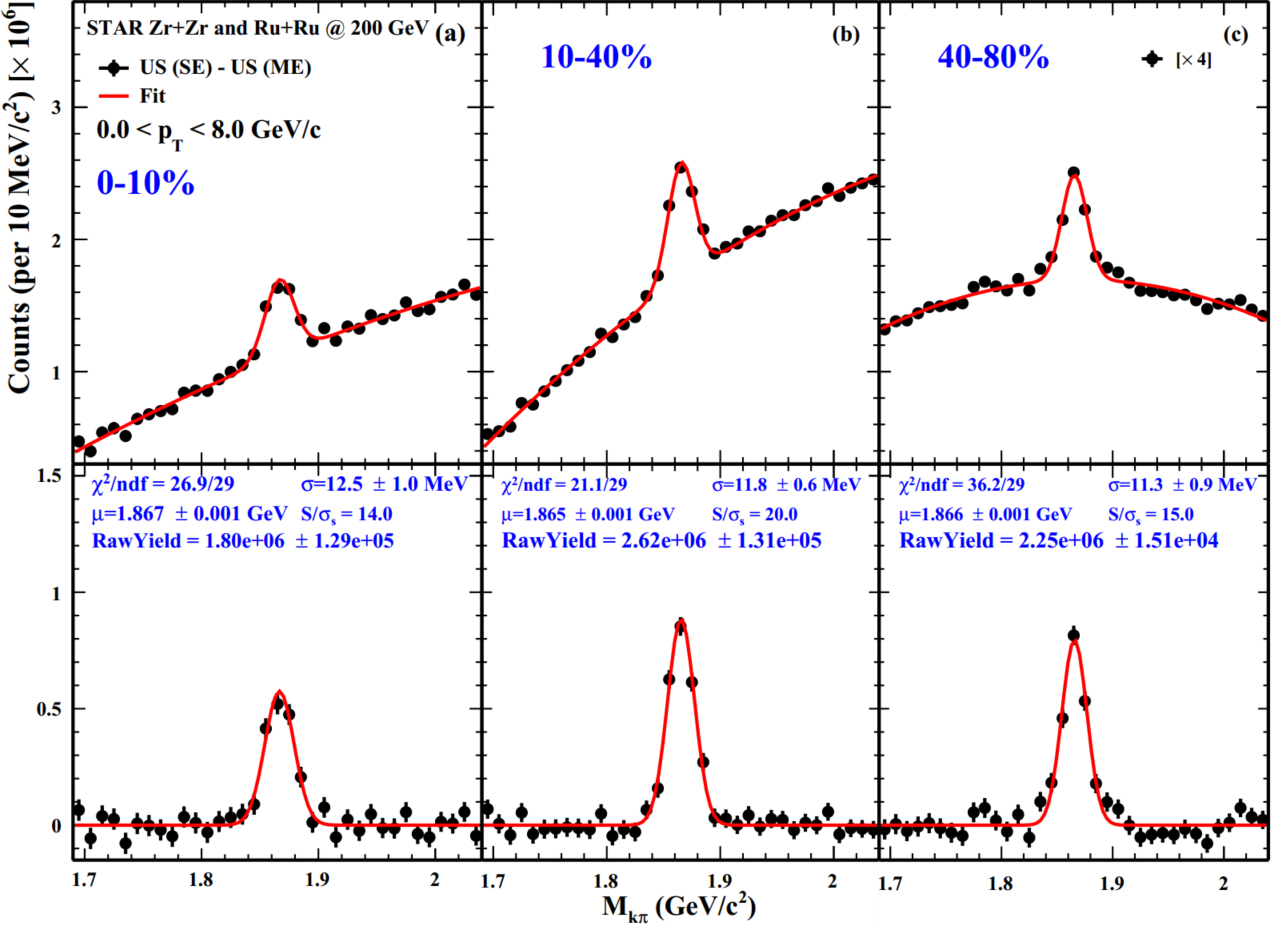
| Figure 2. D0 signal at 0-10% (a), 10-40% (b), 40-80% (c) centrality with transverse momentum range 0-8 GeV/c at mid-rapidity. On the top panel, the solid points show the invariant mass distribution after removing the combination background, and the red line represents a Gaussian and quadratic polynomial combination function fitting. On the bottom panel, the solid points show the D0 signal after the redundant background is removed, and the red line is a Gaussian function fitting to the signal. |
|
|
| Figure 3. D0 invariant yields at mid-rapidity (|y|<1) as a function of pT at 0-10% (black solid circles), 10-40% (red solid squares) and 40-80% (blue solid rhombi) centrality classes in isobar collisions on panel (a). The hollow markers are the result of Au + Au collisions at 200 GeV, which is scaled by a same constant and the ratio of the number of binary collisions between isobar and Au + Au. Levy fits are indicated by the dotted lines. The solid green lines show the p + p reference scaled with the number of binary collisions in isobar system. Panel (b), (c) and (d) respectively show the ratio of data and fitting results at 0-10%,10-40% and 40-80% centrality. |
|
|
| Figure 4. D0 integrated cross section per nucleon-nucleon collision for pT > 0 (top) and pT > 4 GeV/c (bottom) as a function of ⟨Npart⟩. Solid and hollow circles represent isobar and Au + Au collisions, respectively. The error bars represent the statistical uncertainties. The boxes represent the systematic uncertainties. |
|
|
| Figure 5. D0 RAA for 0-10% (top), 10-40% (medium) and 40-80% (bottom) centrality bins in isobar collisions. rhombi are D0 RAA in Au + Au collisions at 200 GeV. The light and dark green boxes on the right depict the normalization uncertainties in determining the Nbin in Au + Au collisions and the total inelastic cross section in p + p collisions, respectively. The dot-dashed lines are model results for isobar collsions. |
|
|
| Figure 6. D0 RAA as a function of ⟨Npart⟩ in isobar collisions (solid circles) and Au + Au collisions (open circles) at 200 GeV. Top and bottom panel are the results of pT > 0 and pT > 4 GeV/c, respectively. The light green boxes on the right depict the normalization uncertainties in determining the Nbin in Au + Au collisions. The blue boxes on the right depict the total uncertainty of inelastic cross section in p + p collisions. |
|
|
| Figure 7. D0 Rcp with the 40-80% spectrum as the reference for 0-10% (a) and 10-40% (b) in isobar collisions at √sNN = 200 GeV compared to corresponding results in Au + Au collisions at 200 GeV. The statistical and systematic uncertainties are shown as error bars and brackets on the data points. |
|
|
| Figure 8. D0 invariant yield at mid-rapidity (|y| < 1) are fitted by mT exponential function for different centrality classes in isobar collisions at √sNN = 200 GeV. The statistical and systematic uncertainties are shown as error bars and brackets on the data points. |
|
|
| Figure 9. Inverse slope parameter Teff obtained from fitting as a function of hadron mass in isobar central collisions (solid red star) and Au + Au central collisions. |
|
|
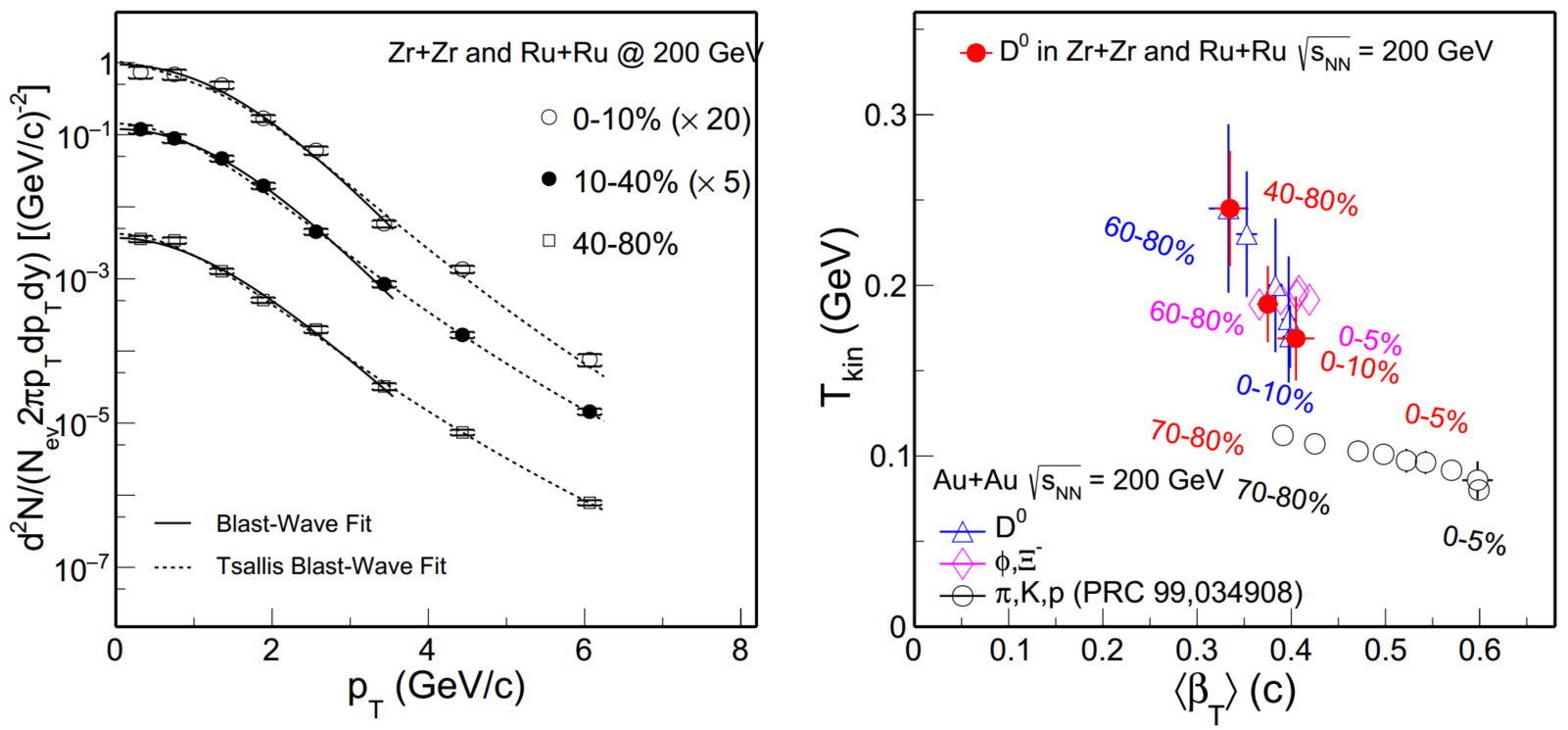
| Figure 10. The BW fitting (solid lines) and the TBW fitting (dash lines) to D0 transverse momentum distributions at various centrality (left). The red solid circles shows D0 Tkin and < β > from BW fitting in isobar collisions (right). And the results of light (open circles), multi-strangeness (pink rhombi), and heavy (blue triangles) flavor hadrons in Au + Au central collisions at 200 GeV are also presented simultaneously. |
Summary:
In summary, we report on measurements of D0 meson production in isobar collisions at √sNN = 200 GeV with the STAR detector at RHIC.
- D0-meson productions are firstly measured at mid-rapidity (|y| < 1) in isobar collisions.
- Nbin-scale effect of the D0 pT spectra between isobar and Au + Au collision within uncertainties is firstly observed.
- The strong suppression D0 nuclear modification factor RAA is also observed for pT > 3 GeV/c in the central isobar collisions.
- No significant systematic dependence of D0 kinetic freeze-out properties in central collisions between isobar and Au + Au collisions within uncertainties is observed.
Related presentations:
Here is a summary of links about related presentations on pwg meeting.
- https://drupal.star.bnl.gov/STAR/system/files/pre_QM_2023_YuanSu.pdf (---New---)
- https://drupal.star.bnl.gov/STAR/system/files/STAR_Collaboration_Meeting_Spring_2023_Yuan_Su.pdf
- https://drupal.star.bnl.gov/STAR/system/files/Paper_Proposal_11172022_v2.pdf
- https://drupal.star.bnl.gov/STAR/system/files/D0_analysis_isobar.pdf
- https://drupal.star.bnl.gov/STAR/system/files/D0_issues_check_07212022.pdf
- https://drupal.star.bnl.gov/STAR/system/files/D0_production_07142022_YuanSu.pdf
- https://drupal.star.bnl.gov/STAR/system/files/D0_Raa_05262022_0.pdf
- suyuann's blog
- Login or register to post comments
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)