Measurement of J/ψ production in Au+Au collisions at sqrt(s_{NN}) = 14.6, 17.3, 19.6 and 27GeV with STAR experiment
Measurement of J/ψ production in Au+Au collisions at √sNN = 14.6, 17.3, 19.6, and 27 GeV with the STAR experiment
PAs: Rongrong Ma, Kaifeng Shen, Zebo Tang, Shuai Yang, Zaochen Ye, Wangmei Zha, Wei Zhang
Target Journal: Phys. Lett. B
Abstract:
We present measurements of inclusive J/ψ production at midrapidity (|y| < 1.0) in Au+Au collisions at √sNN = 14.6, 17.3, 19.6, and 27 GeV, conducted with the STAR detector at the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider. A suppression of J/ψ production is observed in Au+Au collisions at these energies, relative to the scaled production in p+p collisions. Differential measurements of J/ψ RAA are performed as a function of both collision centrality and transverse momentum (pT). In the analysis of centrality dependence, RAA is found to decrease with increasing centrality, with no significant collision energy dependence observed within a similar NPart region. RAA shows an increasing trend with pT, in contrast to results at 200 GeV, where J/ψ RAA exhibits no significant dependence on transverse momentum. Additionally, we measured the collision energy dependence of J/ψ RAA in central collisions, finding no significant energy dependence within uncertainties up to 200 GeV, consistent with transport model calculations.
Figures:
|
|
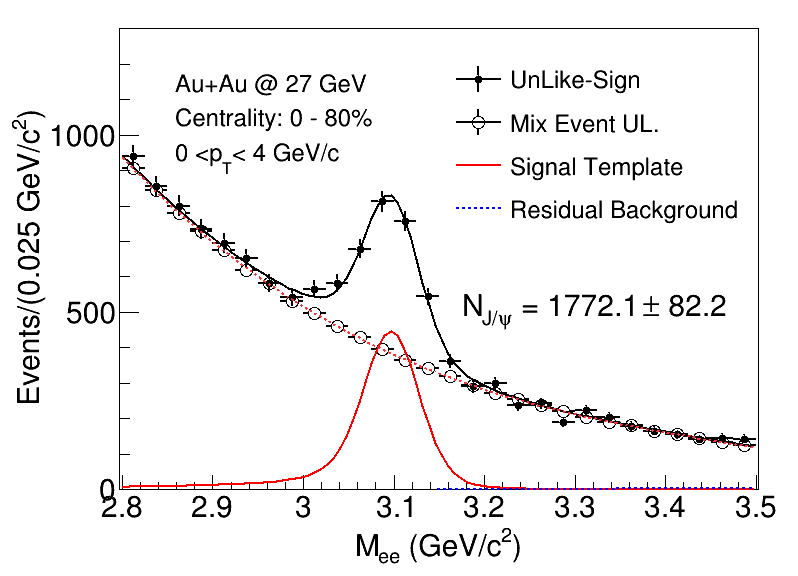
| Figure 1. Invariant mass distributions of J/ψ candidates for pT > 0 GeV/c reconstructed via the di-electron channel at mid-rapidity. The black solid points represent unlike-sign from the same event; The black open circles represent unlike-sign from the mix-event. The red dotted line corresponds to the fit of the unlike-sign from the mixed-event background, while the solid red line represents the signal component. The shape of the J/ψ signal, derived from embedding with additional momentum smearing, is used to fit the di-electron signal, and the residual background is described by a straight line. |
|
|
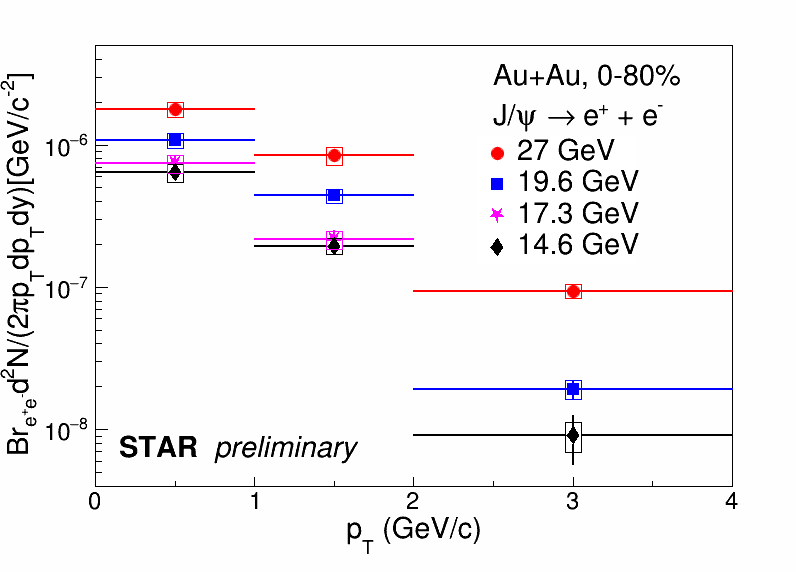
| Figure 2. Inclusive J/ψ invariant yields as a function of pT in Au+Au collisions at √sNN = 14.6, 17.3, 19.6 and 27 GeV. The vertical error bars represent statistical uncertainties, while the boxes represent systematic uncertainties. The horizontal bars indicate the pT bin widths. |
|
|
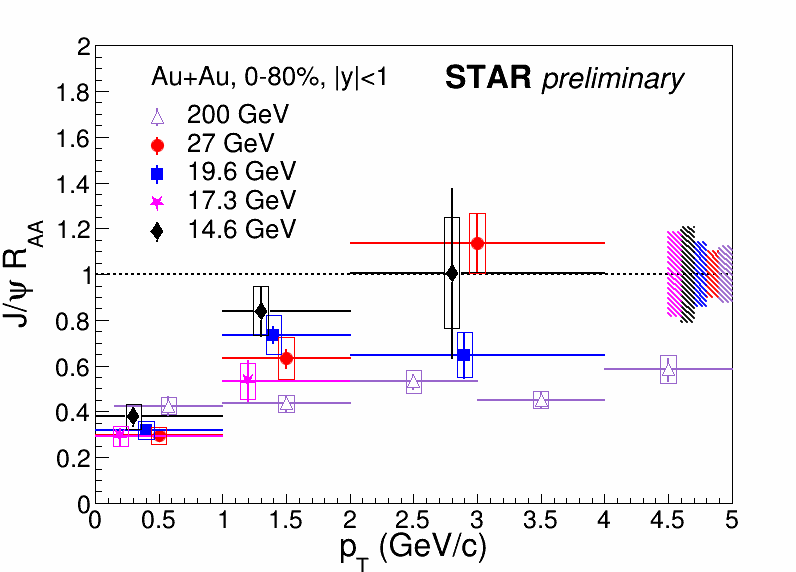
| Figure 3. The inclusive J/ψ RAA as a function of pT at mid-rapidity for Au+Au collisions at √sNN = 14.6, 17.3, 19.6, and 27 GeV is compared to 200 GeV for 0-80% centrality. The error bars represent the statistical uncertainties. The boxes represent the systematic uncertainties. The bands around unity indicate the uncertainties from the TAA and the p+p baselines. A greater suppression is observed at lower pT, and RAA tends to increase with pT. |
|
|
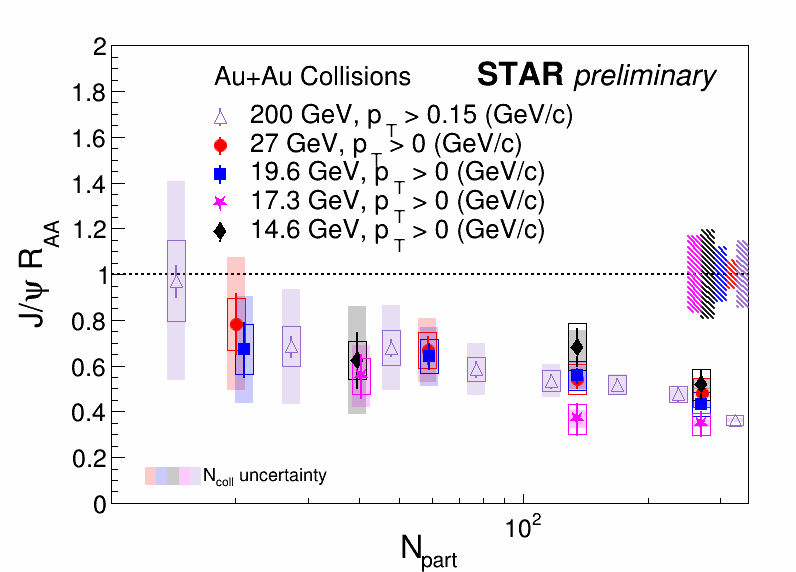
| Figure 4. The RAA of inclusive J/ψ as a function of Npart in Au+Au collisions at √sNN = 14.6, 17.3, 19.6, and 27 GeV is compared to 200 GeV at mid-rapidity. The vertical bars and open boxes around data points represent statistical and systematic uncertainties, respectively. Filled boxes around unity indicate global uncertainties from the p+p baselines. Shaded bands on data points reflect uncertainties from TAA. Suppression of J/ψ production is observed in Au+Au collisions at 14.6, 17.3, 19.6, and 27 GeV. RAA shows no significant energy dependence at RHIC for similar Npart. |
|
|
| Figure 5. The RAA of J/ψ as a function of collision energy for central collisions is compared with two transport model calculations from the Tsinghua group (left) and the TAMU group (right). The vertical bars represent statistical uncertainties, while the open boxes around data points represent systematic uncertainties, including those from the p+p baselines and uncertainties from TAA. |
Summary:
In summary, we report on measurements of J/ψ meson production in Au+Au collisions at √sNN = 14.6, 17.3, 19.6 and 27 GeV with the STAR detector at RHIC.
- The Npart dependence of RAA show a suppression in Au+Au collisions at √sNN = 14.6, 17.3, 19.6 and 27 GeV
- No significant energy dependence of RAA in central collisions from 17.2 to 200 GeV within uncertainties is observed
- A larger suppression is observed at lower pT and towards more central collisions
Related presentations:
Here is a summary of links about related presentations on pwg meeting.
Analysis note:
Paper draft:
- weizhang's blog
- Login or register to post comments
.png)